what is free chlorine in drinking water
During the treatment process chlorine is added to drinking water as elemental chlorine chlorine gas sodium hypochlorite solution or dry calcium hypochlorite. And it does a marvelous job at eliminating most pathogens from the water we drink.

Safe To Drink How Much Chlorine Should Your Water Contain
According to a report from the US.

. It is a widely used disinfectant for drinking water supplies. CDC recommends not exceeding 20 mgL due to taste concerns and chlorine residual decays over time in stored water. Chlorination is the process of adding chlorine to drinking water to kill parasites bacteria and viruses.
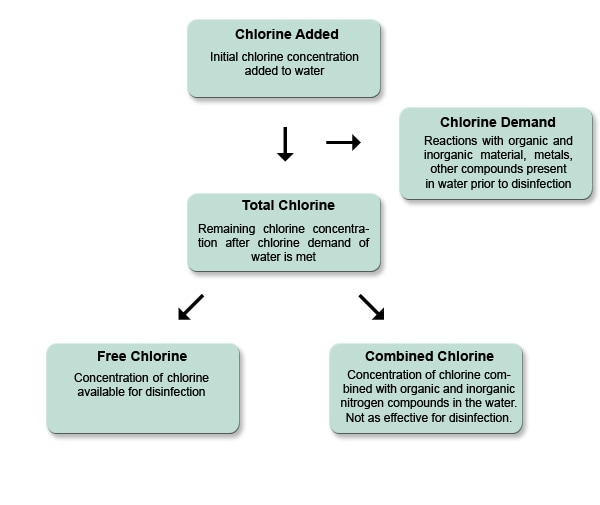
And 2 the water is protected from recontamination during storage. Chloramines have been used by water utilities since the 1930s. Free Chlorine Free chlorine refers to the amount of chlorine that has yet to combine with chlorinated water to effectively sanitize contaminants which means that this chlorine is free to get rid of harmful microorganisms in the water of your swimming pool.
Using or drinking water with small amounts of chlorine does not cause harmful health effects and provides protection against waterborne disease outbreaks. Chloramines also known as secondary disinfection are disinfectants used to treat drinking water and they. The formula of chlorine is free chlorine combined chlorine total chlorine.
Most municipal water systems have chlorine levels. Are most commonly formed when ammonia is added to chlorine to treat drinking water. Chlorinated tap water typically has a high chlorine level and can even taste similar to pool water.
Combined is the chlorine that has mixed with organic matter that has mostly been used up. A free chlorine level of 05 mgLiter of free chlorine will be. Chlorine is used to keep our water clean by disinfecting it and killing germs.
Vitamin C is often used to remove chlorine and chloramine from large amounts of water like pools hot tubs and baths but it can be used in drinking water too. Chlorine levels may vary due to the flow rate of the water in the system your proximity to the water treatment plant and during maintenance periods. Free chlorine residuals of between 0520 mgL provide effective continuous disinfection in water distribution systems.
Chlorination is the process of adding chlorine to drinking water to kill parasites bacteria and viruses. When applied to water each of these forms free chlorine which destroys pathogenic disease-causing organisms. Treating drinking water is not a new process but the transition to chlorination of water sources represents an important shift that had immense public health consequences.
Together the hypochlorous acid and the hypochlorite ions are referred to as free chlorine. Council of Environmental Quality the cancer risk for people who drink chlorinated water is up to 93 higher than for. What chlorine is used in drinking water.
Water that is absolutely pure will only have free chlorine as there is nothing to combine with. Available forms of free chlorine include hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite. Chlorine is a disinfectant commonly used by water utilities.
At this level harmful health effects are unlikely to occur. Total chlorine is the combination of free and combined chlorine. The presence of free chlorine also known as chlorine residual free chlorine residual residual chlorine in drinking water indicates that.
Facilities that receive water from a registered drinking water service provider should ideally receive a free chlorine residual of between 02-05 mgL in. How much chlorine is in our drinking water. Concentration of free chlorine of greater than or equal to 05 mglitre after at least 30 minutes contact time at pH less than 80 This definition is only appropriate when users drink water directly from the flowing tap.
The minimum recommended WHO value for free chlorine residual in treated drinking water is 02 mgL. Different processes can be used to achieve safe levels of chlorine in drinking water. Chlorine levels in drinking water.
Chlorine can be filtered out of drinking water before the point of use with a water treatment system. According to the Centers for Disease Control chlorine levels up to 4 parts per million ppm are considered safe in drinking water. For normal domestic use residual chlorine levels at the point where the consumer collects water should be between 02 and 05 mgl.
Different processes can be used to achieve safe levels of chlorine in drinking water. What should free chlorine level be in drinking water. Chlorine has an odour threshold in drinking water of about 06 milligrams per litre mgL but some people are particularly sensitive and can detect amounts as low as 02 mgL.
Chlorine dissociates in water to form free chlorine to kill harmful microorganisms. Free chlorine can be measured with a test kit a checker colorimeter portable photometers and benchtop meters. Free is the chlorine that is ready to fight bacteria and other microbes.
Chlorine is added to drinking water to protect against harmful microbes and waterborne diseases. Using or drinking water with small amounts of chlorine does not cause harmful health effects and provides protection against waterborne disease outbreaks. Hypchlorous acid is the more effective disinfectant and therefore a lower pH is preferred for disinfection.
But the use of this powerful chemical has a downside. Provide longer-lasting disinfection as the water moves through pipes to consumers. The downside is you need to buy vitamin C tablets or powder and it can decrease the pH levels of the water but if used in small quantities its suitable for fermentation.
1 a sufficient amount of chlorine was added initially to the water to inactivate the bacteria and some viruses that cause diarrheal disease. A pH between 65 and 85 will see both hypochlorous acid and hypochlorite ions present in the water. Chlorine and free chlorine residual.
Free Chlorine refers to the amount of chlorine that is floating around in solution that is still available to sanitize. Normal chlorine concentrations in scheme drinking water supplies in Western Australia usually range from 05 to 15 milligrams per litre. The higher level will be close to the disinfection point and the lower level at the far extremities of the supply network.

Concentrations Of Free Combined And Total Chlorine In The Drinking Download Scientific Diagram

Citizens Across The Country Question Chloramines In Drinking Water Ensia

Residual Chlorine Levels Mg L In Drinking Water Among Developed Download Scientific Diagram

Chlorine Water Facts Is The Chlorine In Water Bad For You

Disinfection Breakpoint Chlorination Youtube

How To Analyze Free Chlorine Residual Youtube

Does Boiling Remove Chlorine How To Dechlorinate Water

Effects Of Drinking Chlorine Water Is It Safe Detox Cure

Chlorinated Tap Water Shop 57 Off Www Ingeniovirtual Com

Trends And Effects Of Chloramine In Drinking Water Wcp Online
Chlorine Residual Testing The Safe Water System Cdc

Chlorine In Drinking Water The Good The Bad And The Ugly Springwell Water Filtration Systems

Free Vs Combined Vs Total Chlorine What S The Difference Atlas Scientific

Is It Safe To Supply Drinking Water Chlorine Free Water Technology
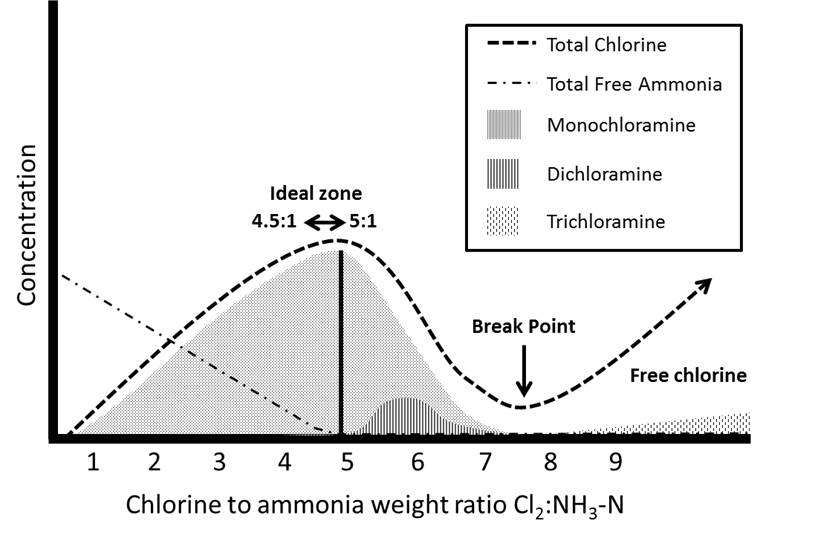
Chloramines In Drinking Water Guideline Technical Document For Public Consultation Canada Ca

Chlorinated Tap Water Shop 57 Off Www Ingeniovirtual Com
How Much Chlorine Is In Tap Water Flowater

